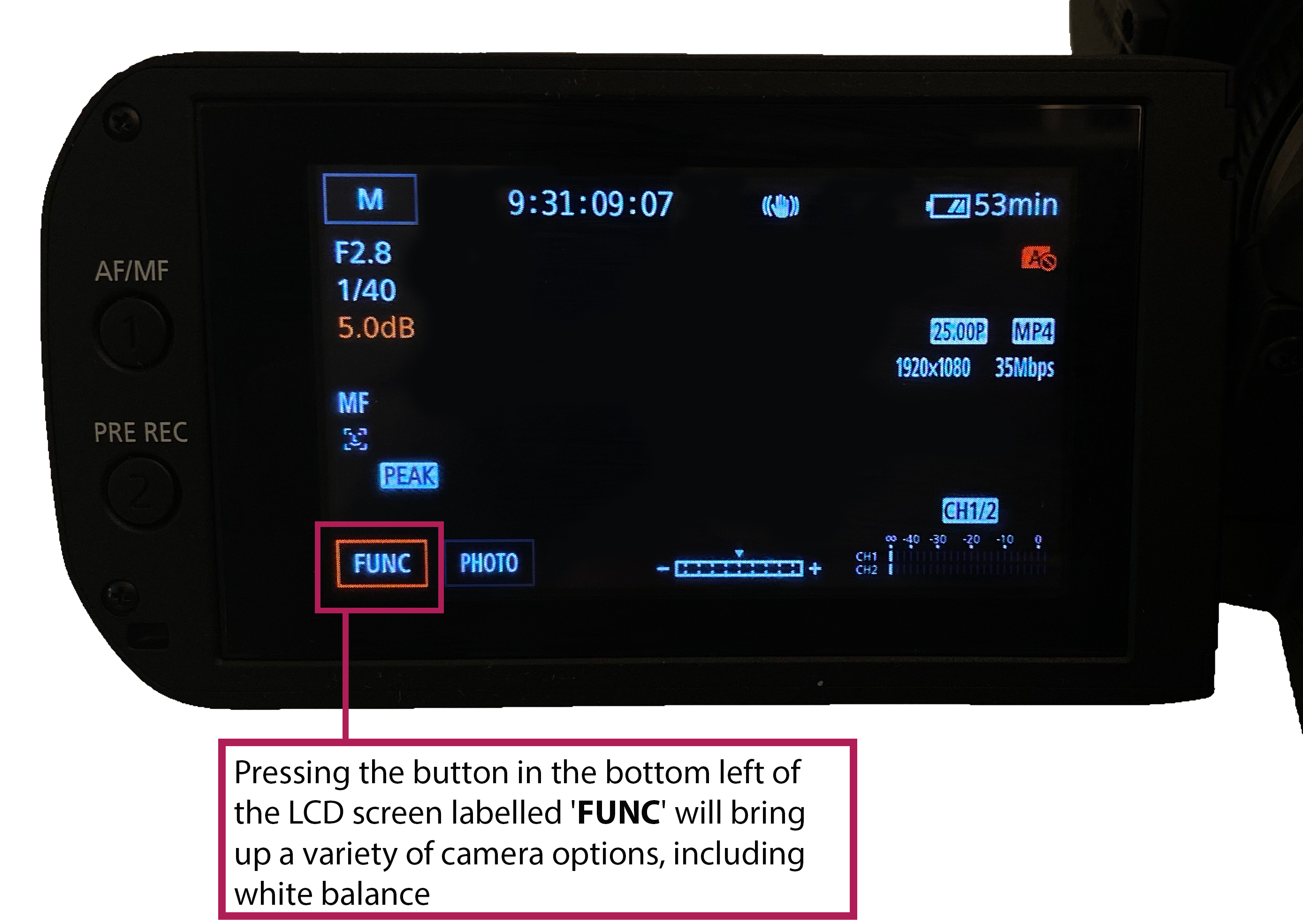
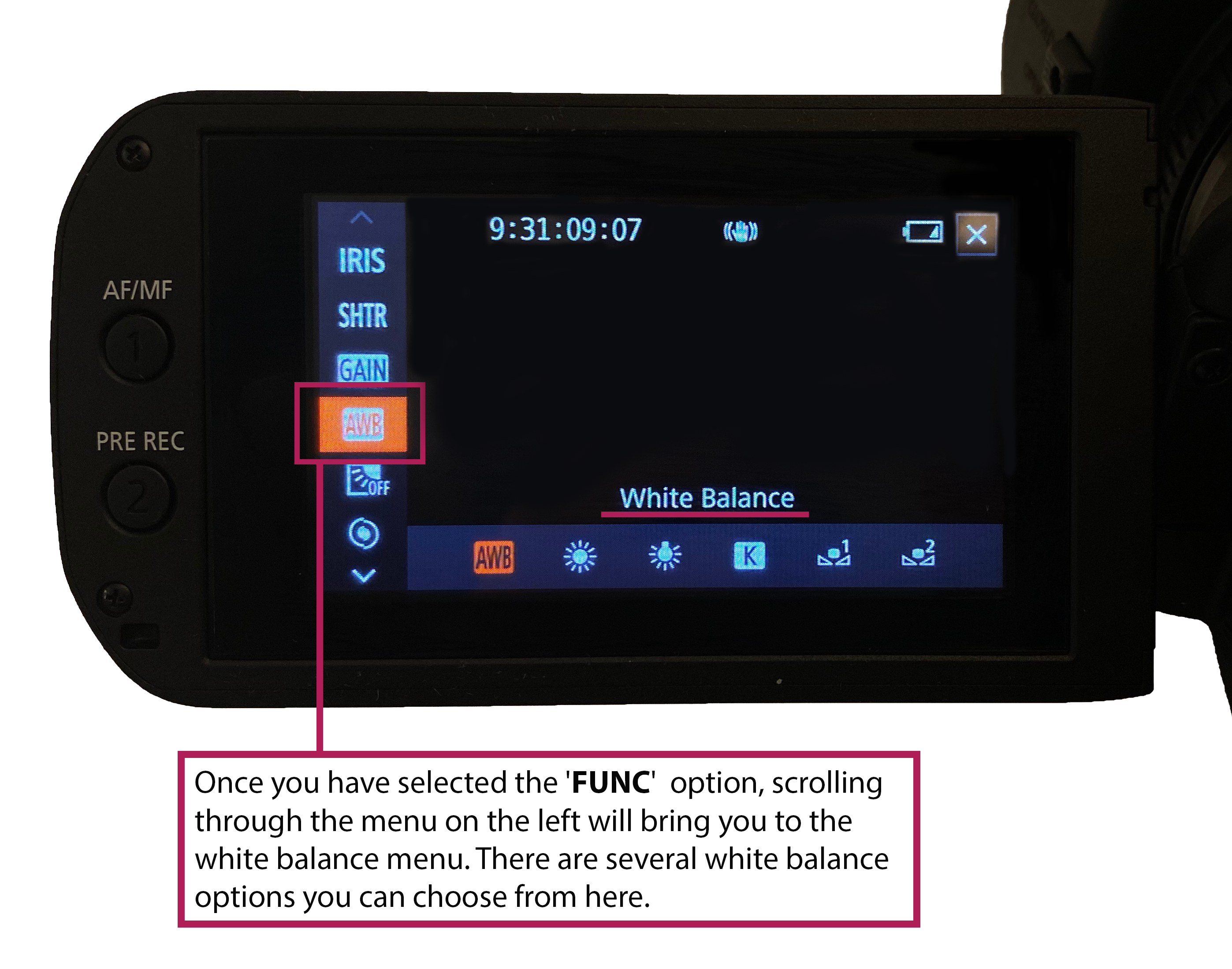
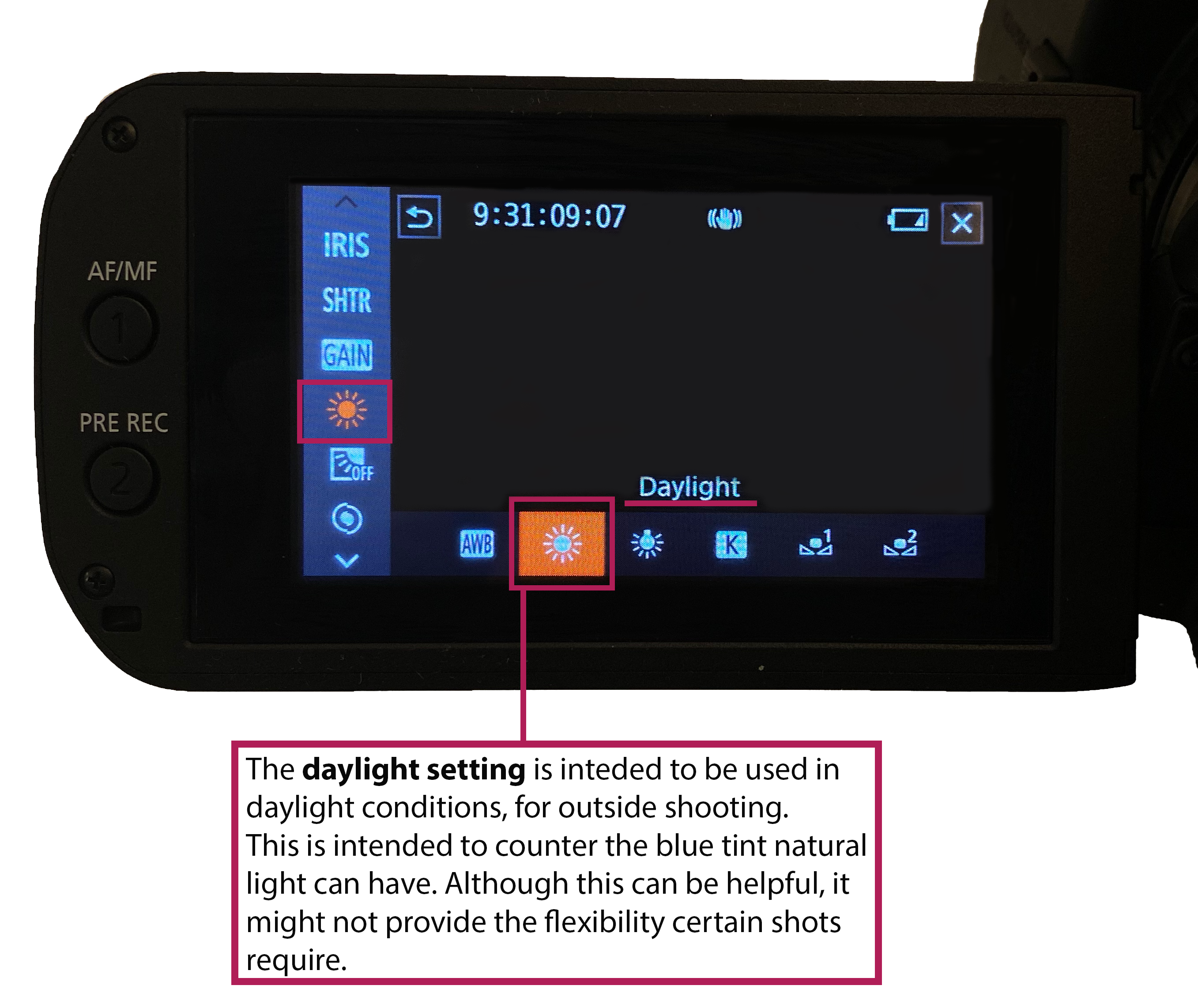
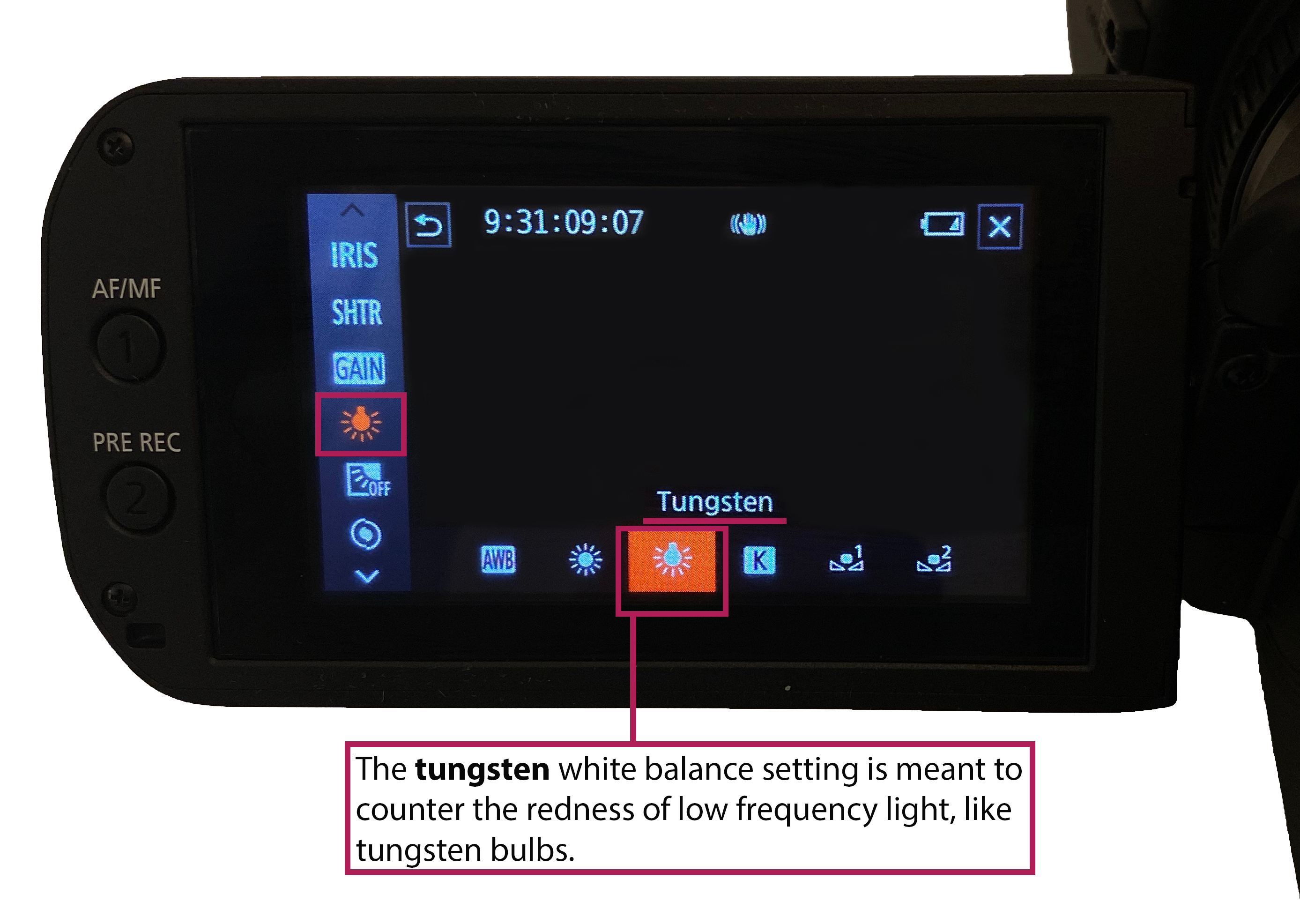
This article is an introduction to white balance, what it is and what correctly white balancing does to the images you produce. This guide can be applied to both digital video cameras and digital stills cameras.
What is white balancing?
White balancing is the process of telling your camera “this object is white”
Have you ever taken a picture and noticed that what you can see with your eye and what the camera has recorded are slightly different? Or noticed how under different lights, colours appear differently?
The colours your camera picks up can differ from what is actually seen by the human eye. This is because of the colour temperature of different light sources. This is measured in degrees Kelvin and is represented with a K.
Light with a higher colour temperature will appear more blue and have a larger Kelvin value.
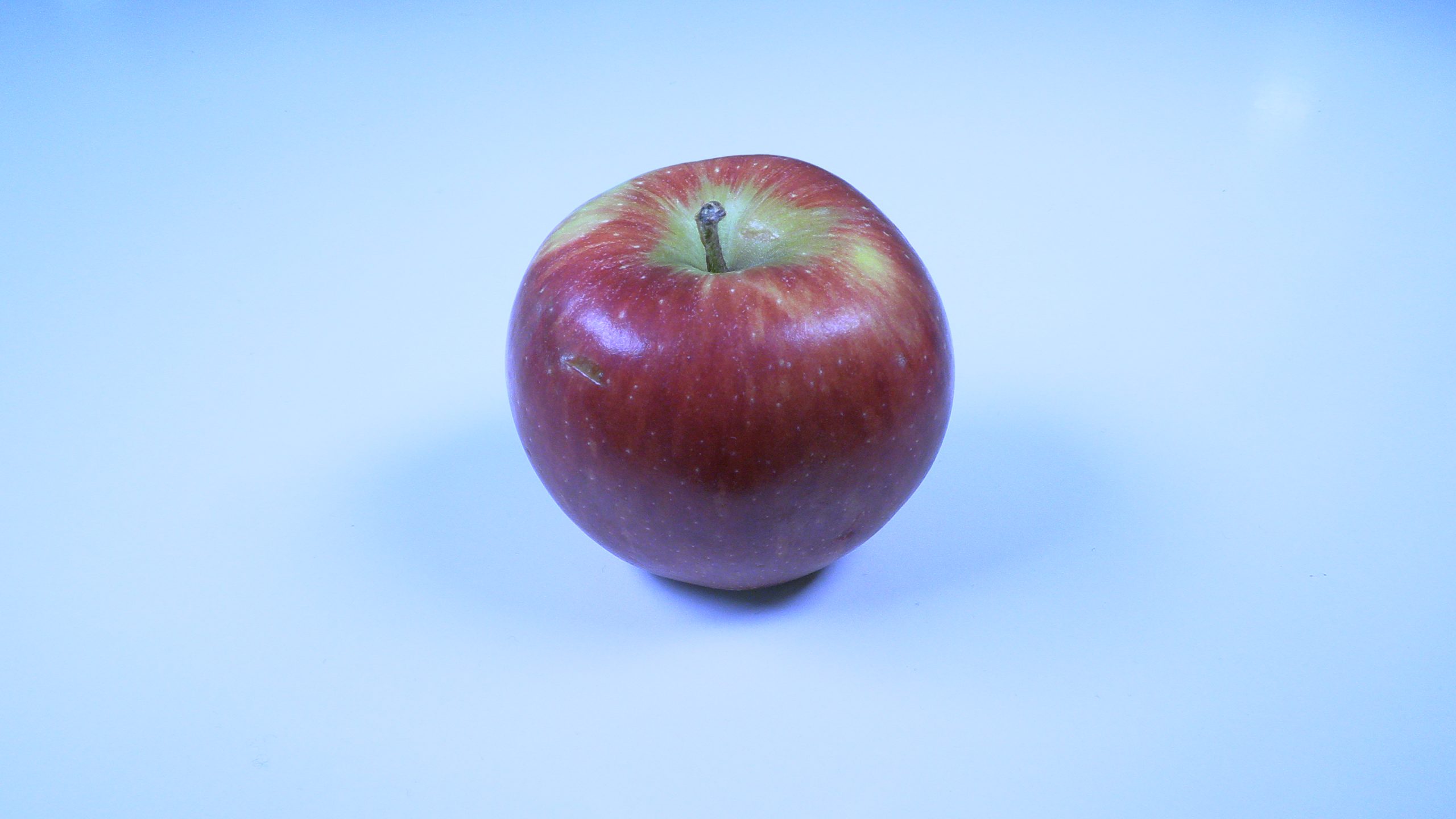

Light with a lower colour temperature will appear redder and have a smaller Kelvin value. Natural daylight tends to have a higher Kelvin value than artificial light.
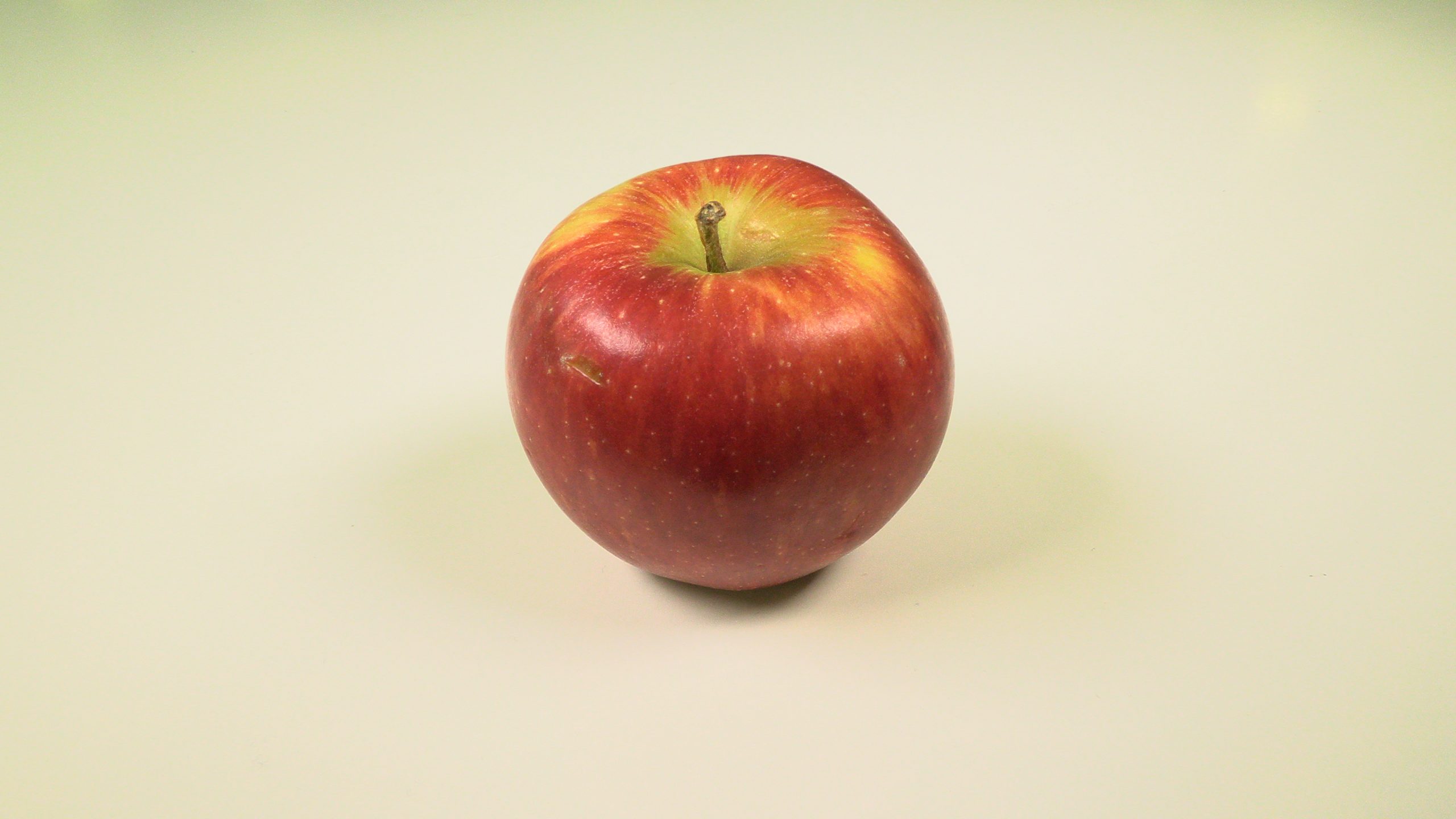

Natural light picture
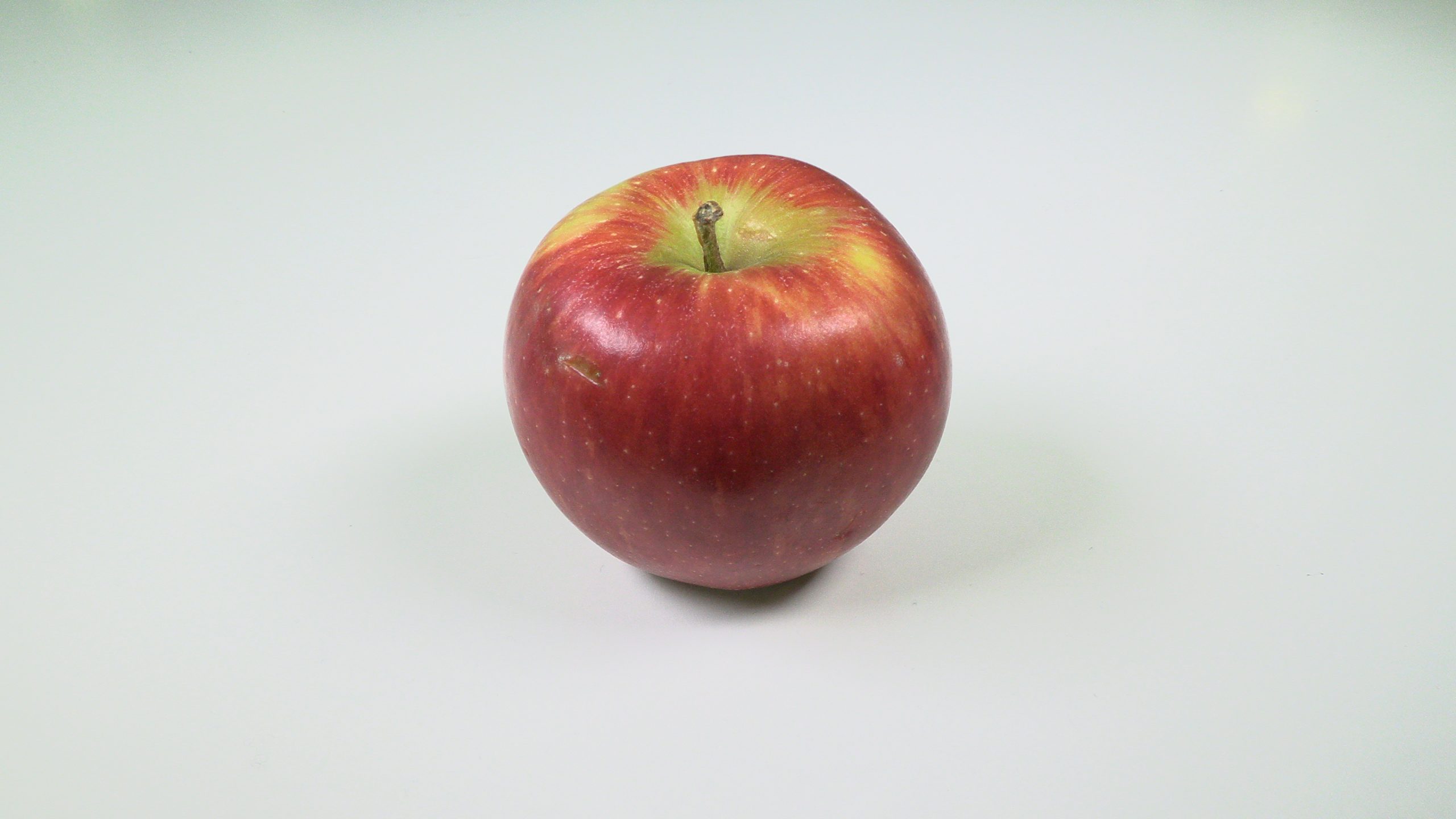

These differing colour temperatures can leave what’s called colour casts on images. This means that the entire image has a blue, orange or green tint to it.
White balancing is the process of telling the camera’s digital sensor “this object is white”. This will yield images that are much closer to what the human eye can see and should reduce colour inconsistencies between shots. As a result, any post-production work you do on your photos or videos likely be easier.
How do I white balance?